|
|
|
Publications on the Web
This is an annotated list of papers, reviews, grants, and abstracts by R. W.
Williams and colleagues.
List of Contents
Quantitative Neurogenetics & QTL Mapping
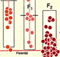
 An example of a hippocampus
used for gene mapping. This dissection is from the left hemisphere. Five
cross-sections illustrate internal structure. For more details on this
work and information on QTLs that control hippocampal size and structure,
see the article Genetic Control of Neuron Number below. An example of a hippocampus
used for gene mapping. This dissection is from the left hemisphere. Five
cross-sections illustrate internal structure. For more details on this
work and information on QTLs that control hippocampal size and structure,
see the article Genetic Control of Neuron Number below.
List of Contents
Genetics of Myopia
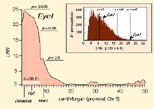 The Eye1 locus. Linkage between
variation in eye weight and proximal Chr 5. The x-axis represents the
entire genetic length of Chr 5—from the proximal end (left) near marker
D5Mit346 to the distal end of the chromosome at approximately 60 cM (far
right). The y-axis represents the strength of linkage assessed using the
likelihood ratio statistic (LRS) computed at 1 cM intervals using an
interval mapping procedure without any adjustment for secondary QTLs using
data for the 26 BXD strains. The Eye1 locus. Linkage between
variation in eye weight and proximal Chr 5. The x-axis represents the
entire genetic length of Chr 5—from the proximal end (left) near marker
D5Mit346 to the distal end of the chromosome at approximately 60 cM (far
right). The y-axis represents the strength of linkage assessed using the
likelihood ratio statistic (LRS) computed at 1 cM intervals using an
interval mapping procedure without any adjustment for secondary QTLs using
data for the 26 BXD strains.
List of Contents
Control of Neuron Number and Stereology
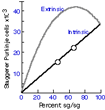 Two theoretical curves that
illustrate the expected number of sg/sg genotype Purkinje cells (PC) in sg/sg
by +/+ chimeras, assuming two different modes of gene action (see Herrup &
Mullen 1981 for the assumptions and calculations on which these curves are
based). Two theoretical curves that
illustrate the expected number of sg/sg genotype Purkinje cells (PC) in sg/sg
by +/+ chimeras, assuming two different modes of gene action (see Herrup &
Mullen 1981 for the assumptions and calculations on which these curves are
based).
List of Contents
Growth Cones and Dying Axons
 This monster took the better
part of three years to complete. The web edition has been updated with
new figures (including color-tinted electron micrographs). If you would
like to see high-resolution images of growth cones and dying axons, this
is a great source. The paper was published in The Journal of Comparative
Neurology in 1986 by R. W. Williams, Michael Bastiani, Barry Lia, and
Leo Chalupa. We show that about 80% of all retinal ganglion cells die
early in development in domestic cats. The paper has a fairly long
discussion on the developmental significance (and insignificance) of
neuron death. This monster took the better
part of three years to complete. The web edition has been updated with
new figures (including color-tinted electron micrographs). If you would
like to see high-resolution images of growth cones and dying axons, this
is a great source. The paper was published in The Journal of Comparative
Neurology in 1986 by R. W. Williams, Michael Bastiani, Barry Lia, and
Leo Chalupa. We show that about 80% of all retinal ganglion cells die
early in development in domestic cats. The paper has a fairly long
discussion on the developmental significance (and insignificance) of
neuron death.
List of Contents
Retinal Developmental and Visual System Mutants
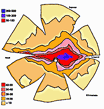 The distribution of retinal
ganglion cells in the cat's retina. Colors are used to indicate cell
packing density. The area centralis (dark blue region) contains as many
as 8,600 cells/mm2. Cell densities are particularly high along the
hroizontal axes from the temporal periphery (right) to the nasal
periphery (left). If you select the image you may view an enlarged
version with overlaid cell counts per 0.058 µm2 (multiply by 17.24 to
obtain cell densities per mm2). The distribution of retinal
ganglion cells in the cat's retina. Colors are used to indicate cell
packing density. The area centralis (dark blue region) contains as many
as 8,600 cells/mm2. Cell densities are particularly high along the
hroizontal axes from the temporal periphery (right) to the nasal
periphery (left). If you select the image you may view an enlarged
version with overlaid cell counts per 0.058 µm2 (multiply by 17.24 to
obtain cell densities per mm2).
List of Contents
Grant Applications
The full text of a 1995 NSF grant submission
that outlines our research objectives and methods. The focus is on mapping
quantitative trait loci that affect CNS development.
The full text of a project now funded by the Human Brain Project to continue
the development of the Informatics Center for Mouse Neurogenetics (funding
from 2000 to 2004).
List of Contents
A 1990 U.S. Patent
A patent for a system to accurately count
numbers of cells or particles in a section or sample of tissue.
List of Contents
Most Recent
Abstracts
| |
2000 |
Williams RW, Lu L,
Airey DC, Kulkarni K, Manly KF, Zhou G, Threadgill DW (2000) RIX
mapping: A demonstration using CXB RIX hybrids to map QTLs modulating
eye size in mice.
Int Mouse Genome Conf 14: XX. |
| |
2000 |
Williams RW, Lu L,
Airey DC, Kulkarni K, Manly KF, Zhou G, Threadgill DW (2000) RIX
mapping: A demonstration using CXB RIX hybrids to map QTLs modulating
eye size in mice. Rosen GD, Williams AG, Capra JA, Connolly MT, Cruz
B, Lu L, Airey DC, Kulkarni K, Williams RW (2000) The Mouse Brain
Library @ www.mbl.org.
Int Mouse Genome Conf 14: XX |
| |
2001 |
Lu L, Airey DC,
Williams RW (2001) Genetic architecture of the mouse hippocampus:
Identification of gene loci with regional effects.
31st Annual Neuroscience meeting:XX |
|
|
|

 Publications
Publications Page maintained by R.Williams | A.Centeno. Last
updated:
Page maintained by R.Williams | A.Centeno. Last
updated: