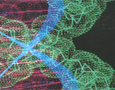
 The scientific motivation
for this program project is to investigate the complex
network of molecules and mechanisms that modulate the
structure of different parts of the brain from major
subdivisions such as the hippocampus, thalamus, and
cerebellum, down to the level of discrete subpopulations
of neurons and glial cells in single nuclei. The scientific motivation
for this program project is to investigate the complex
network of molecules and mechanisms that modulate the
structure of different parts of the brain from major
subdivisions such as the hippocampus, thalamus, and
cerebellum, down to the level of discrete subpopulations
of neurons and glial cells in single nuclei.
The bioinformatic tools and resources that we have been creating have very wide applicability, but our program
project is specifically directed at exploiting a powerful new reductionist approach to explore the genetic basis of the
very significant structural differences between the brains of different strains of mice. (Informatics Center for Mouse Neurogenetics).
|
.gif) |
 |
GeneNetwork Trait Correlation Upgrade. The most important innovation from the user's point-of-view is a fast method to compute correlations among transcripts that reduces the response latency about 20-fold--from 90 seconds to under 5 seconds using standard Affymetrix and Illumina data sets consisting of 45000 probes or probe sets. Of even greater importance, this improvement means that GN can now handle massive Affymetrix Exon 1.0 ST data sets that have over 1.1 million probe sets in about 60 seconds. The new method exploits a set of text files that are external to the database (essentially a materialized view), parallel computing technique (Parallel Python) and optimized SQL queries. more |
.gif) |
 |
Now Available GenomeMixer is a cross-platform application that allows
you to simulate complex multi-generational breeding schemes. GenomeMixer will handle up to 20,000
parental strains. The number and length of chromosomes is fully editable, and you should be able to
model almost any sexually reproducing diploid species. All you have to do is input the length and number
of chromosomes, the names of the purbred strains, and an arbitrary breeding scheme, and GenomeMixer will
output the simulated genetic results of such a cross... more |
 |
Gumbo 2.6
- The iScope "internet microscope" is a complete system for Internet microscopy. Located at the University
of Tennessee in Memphis, the system uses three Zeiss Universal microscopes to provide online, realtime access
to the slides which form the Mouse Brain
Library. Secure user authentication and scheduling ensures reliable,
responsive access to the system... more | watch movie tutorial |
 |
After using Gumbo to request that specific areas of a slide be imaged, "Aria 3-D"
(Automated Remote Image Analysis) is used to browse through and view these movies. Aria 3-D doesn't
directly interface with the microscopes; it downloads previously-generated movies from the iScope server,
and allows you to rapidly focus through them and count cells. Since movie queuing is disabled in the current
version of Gumbo you will be able to view movies from our library, but not request your own. ...
more |
See Movie Tutorial (require flash) |
 |
Sep 17th 2003 -
A collection of high magnification electron micrographs of the mouse optic nerve suitable for quantitative, comparative, and
genetic analysis... more |
 |
Aug 19th 2003 -
BXD Phenotype Database (or download Excel or tab-delimited
text files). Our thanks to John Belknap and the Portland
group for providing an extensive file that
catalyzed this BXD phenotype database. Portland-derived
data in the BXD database are currently (Aug 2003) being
edited and updated by John Crabbe and colleagues and
many new phenotypes are being
added. We will soon provide a link to this new phenome
database. Queries about specific Portland-derived phenotypes
can be directed to Mark Rutledge-Gorman. (By Elissa Chesler
and Mary-Kathleen Sullivan; updated Aug 19, 2003 by RW)
Browse |
Excel File |
.gif) |
 |
WebQTL Demonstration - In this demonstration, we explore one important transcript
expressed in the brain: the amyloid beta precursor protein messenger RNA. The product of this mRNA,
the APP protein, is associated with Alzheimer disease. Part 1: How to discover shared expression patterns (slides 2-14)
Part 2. Discovering upstream modulators (15-25) Part 3. Discovering downstream targets... More
|
 |
The collection now consists of images from approximately 1500 brains Search
the library You can search the MBL for cases by strain, age, sex, body or brain weight.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|

 News & Updates
News & Updates Page maintained by R.Williams | A.Centeno. Last
updated:
Page maintained by R.Williams | A.Centeno. Last
updated: